Situation
Modern agriculture faces challenges in efficient management and sustainable production, requiring precise, timely, and comprehensive information on crop and soil conditions
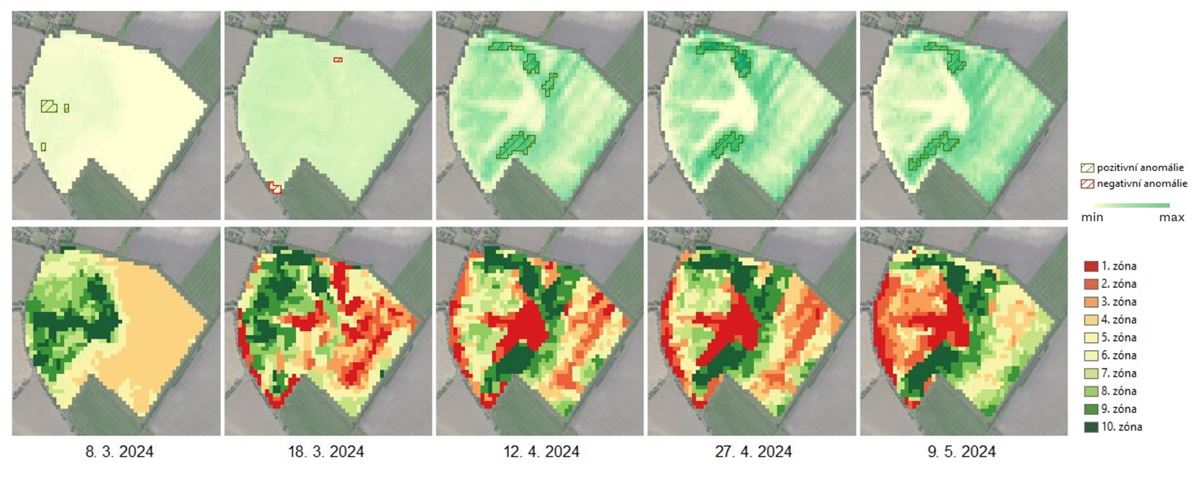
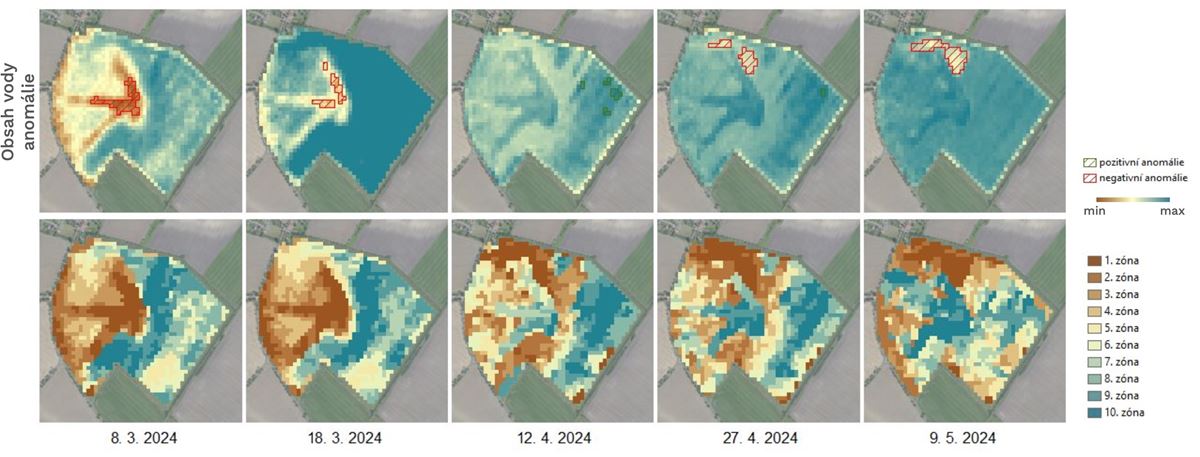
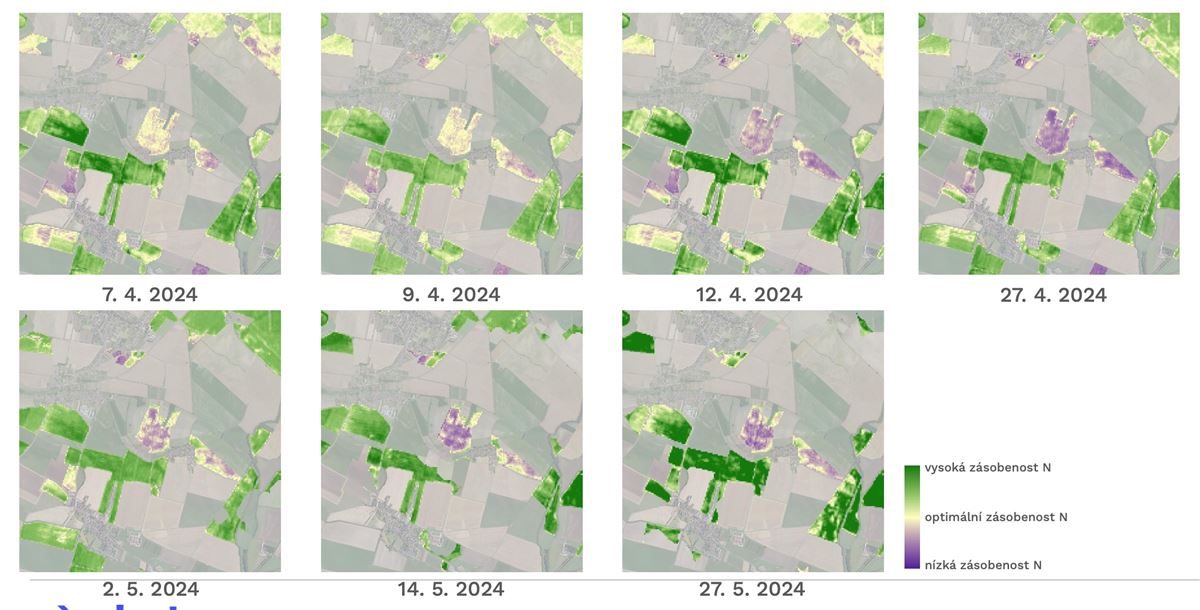
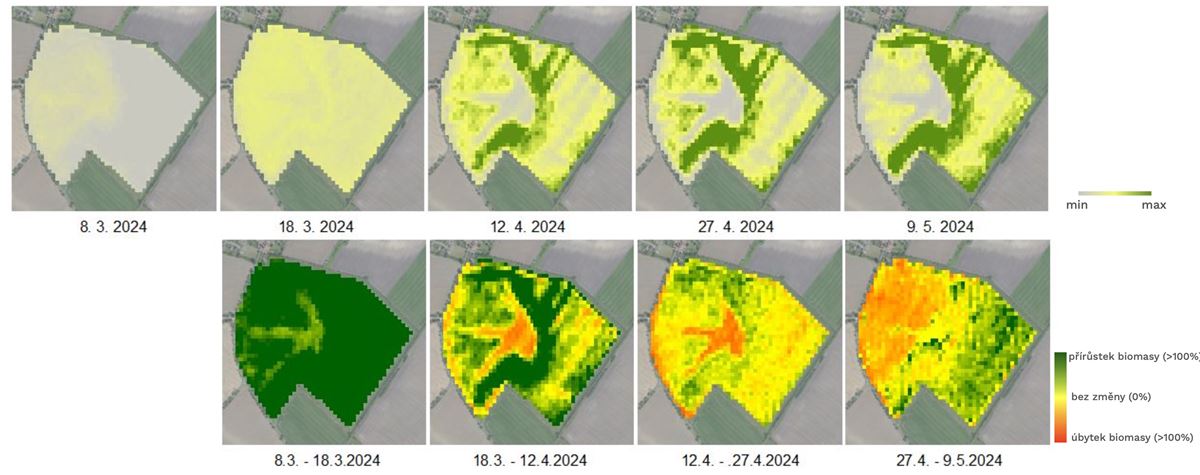
Farmers and agronomists need reliable data to optimize agrotechnical practices, target input use, and minimize environmental impacts. A common issue when working with optical satellite data is incomplete coverage of target areas due to cloud cover, which can lead to data gaps and complicate interpretation and use for continuous monitoring and decision-making.
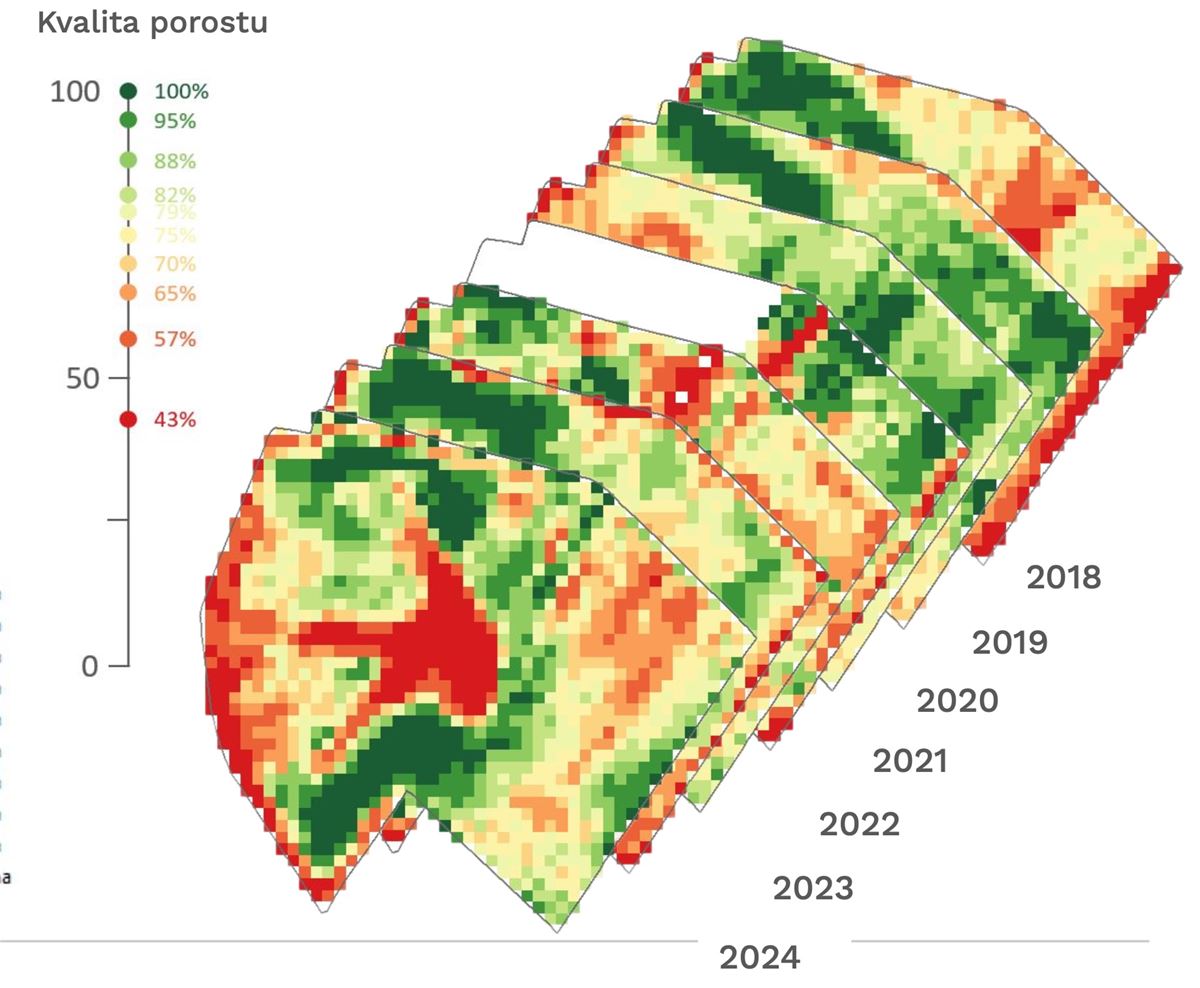
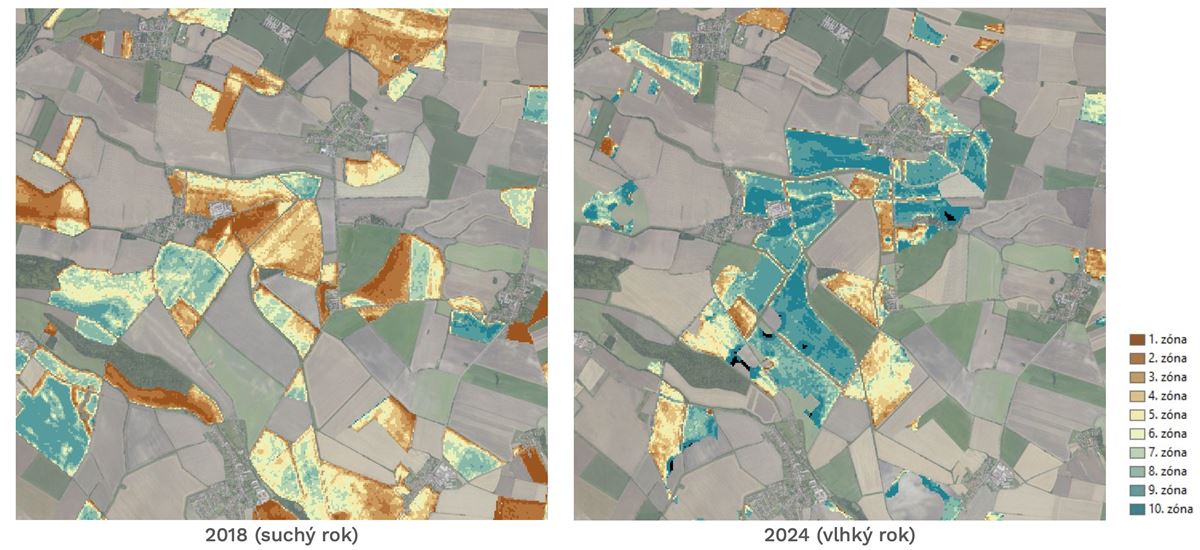
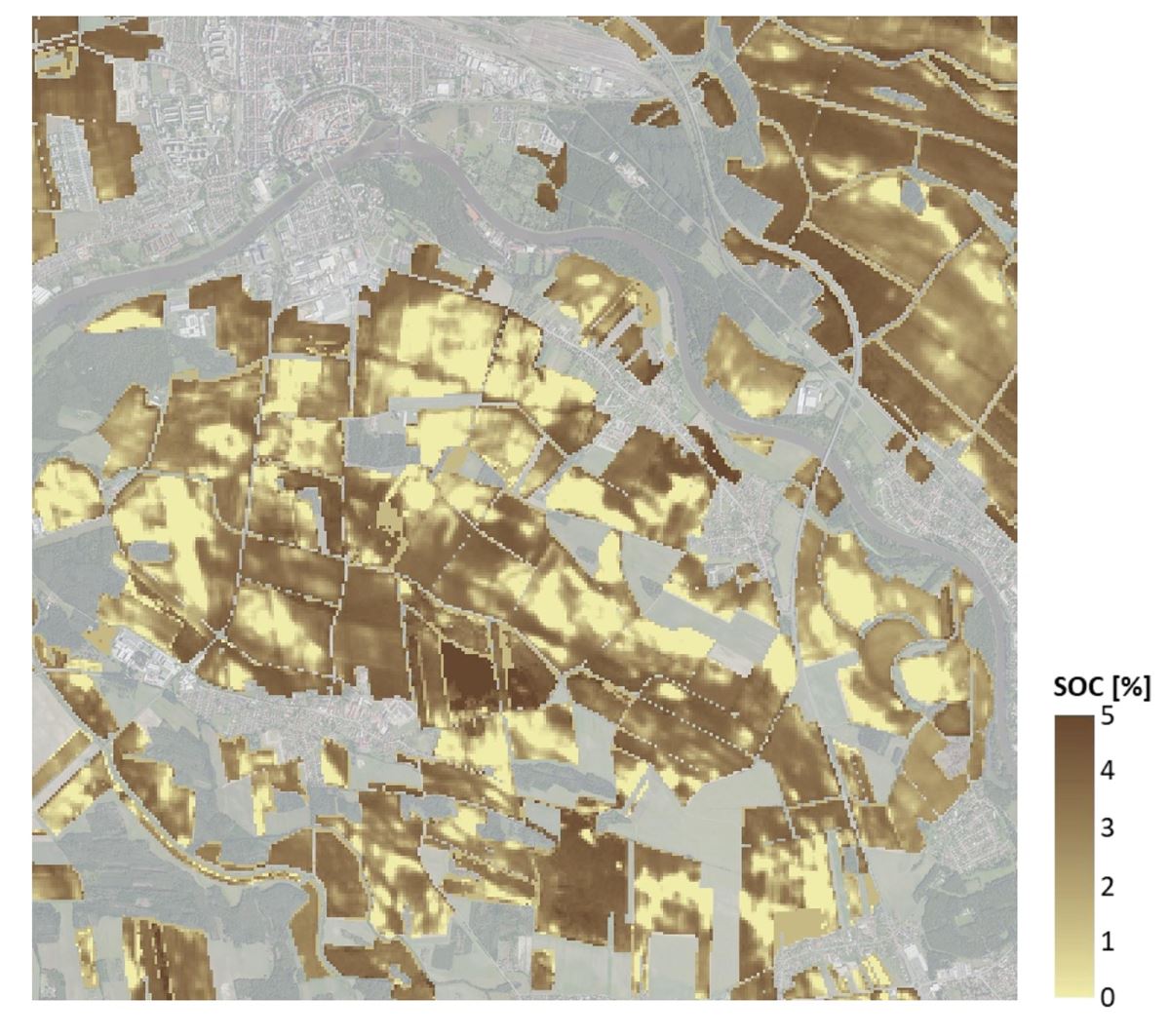
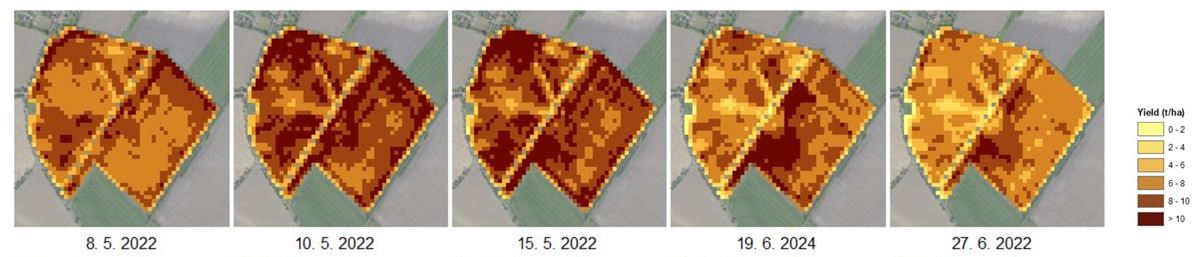
Consequently, there is a clear demand for consistent, regularly updated, and easily interpretable geospatial products that integrate the latest advances in Earth Observation and provide specific, tailored information for variable-rate applications, yield prediction, assessment of crop nutritional status and water regime, and long-term soil quality monitoring.